10th Grade > Physics
ELECTRICITY MCQs
Total Questions : 244
| Page 1 of 25 pages
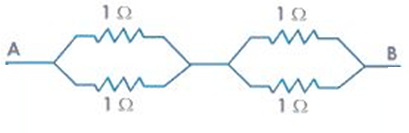
Answer: Option B. -> 1 Ω
:
B
Two parallel combination of resistors:
When going from A to B, the firsttwo resistors are in parallel to each other and so are the next two. Therefore
Rparallel =1×11+1= 12Ω for both of them.
Now these equivalent resistors are in series with each other
Therefore, net equivalent resistance is:
R=0.5+0.5=1Ω
:
B
Two parallel combination of resistors:
When going from A to B, the firsttwo resistors are in parallel to each other and so are the next two. Therefore
Rparallel =1×11+1= 12Ω for both of them.
Now these equivalent resistors are in series with each other
Therefore, net equivalent resistance is:
R=0.5+0.5=1Ω
Answer: Option C. -> 3
:
C
All electric cells have two terminals, positive and negative terminal. If two cells are connected with opposite polarities as shown, the net potential difference across them is the difference of the individual EMFs of the cells.. Hence, there is no net potential difference in the case the cells are identical. Therefore, current will not flow and the bulb will not glow.
:
C
All electric cells have two terminals, positive and negative terminal. If two cells are connected with opposite polarities as shown, the net potential difference across them is the difference of the individual EMFs of the cells.. Hence, there is no net potential difference in the case the cells are identical. Therefore, current will not flow and the bulb will not glow.
Answer: Option C. -> H∝I2
:
C
According to Joule's law, theheat produced in a resistor is;
(i) directly proportional to the square of current for a given resistance.
(ii) directly proportional to resistance for a given current.
(iii) directly proportional to the time for which the current flows through the resistor.
That is H=I2×R×t
HenceH∝I2 is the right relation.
:
C
According to Joule's law, theheat produced in a resistor is;
(i) directly proportional to the square of current for a given resistance.
(ii) directly proportional to resistance for a given current.
(iii) directly proportional to the time for which the current flows through the resistor.
That is H=I2×R×t
HenceH∝I2 is the right relation.
Answer: Option B. -> False
:
B
In alloys,the increase in temperature results in an increase of its resistance, but unlike pure metals, the increase is relatively small and irregular.As the temperature increases, the molecules in the atom vibrate with more frequency, they collide with each other more frequently which makes it tough for the movement of free electrons. Thus the resistance increase with increasing temperature in the metal.
:
B
In alloys,the increase in temperature results in an increase of its resistance, but unlike pure metals, the increase is relatively small and irregular.As the temperature increases, the molecules in the atom vibrate with more frequency, they collide with each other more frequently which makes it tough for the movement of free electrons. Thus the resistance increase with increasing temperature in the metal.
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
Resistivity depends on temperature. Withthe increasein temperature, the random motion of electrons increases. Asa result, the number of collisions of electrons with the positive ions increases. Hence, the resistivity of all pure metals increases with the rise in temperature and decreases with the decrease in temperature.
:
A
Resistivity depends on temperature. Withthe increasein temperature, the random motion of electrons increases. Asa result, the number of collisions of electrons with the positive ions increases. Hence, the resistivity of all pure metals increases with the rise in temperature and decreases with the decrease in temperature.
Answer: Option A. -> R
:
A
The connection of wires is as shown below.
 We have to calculate equivalent resistance across the opposite corners i.e. across Aand Dor Band C. If we take two corners B and C, then we can clearly see that the resistances of AB and AC, and CD and BD are in series.
We have to calculate equivalent resistance across the opposite corners i.e. across Aand Dor Band C. If we take two corners B and C, then we can clearly see that the resistances of AB and AC, and CD and BD are in series.
So the equivalent resistance across CAB is 2R ( CA and AB are in series) and CDB is also 2R ( CD and BD are in series).
The two equivalent resistances across CAB and CDB are in parallel. Hence, the equivalent resistance across the two corners i.e. B and Cis 1Req=12R+12R.
On solving we get, Req=R. Similarly, equivalent resistance across Aand Dwill also beR.
Hence the equivalent resistance across the opposite corners is R.
:
A
The connection of wires is as shown below.
 We have to calculate equivalent resistance across the opposite corners i.e. across Aand Dor Band C. If we take two corners B and C, then we can clearly see that the resistances of AB and AC, and CD and BD are in series.
We have to calculate equivalent resistance across the opposite corners i.e. across Aand Dor Band C. If we take two corners B and C, then we can clearly see that the resistances of AB and AC, and CD and BD are in series.So the equivalent resistance across CAB is 2R ( CA and AB are in series) and CDB is also 2R ( CD and BD are in series).
The two equivalent resistances across CAB and CDB are in parallel. Hence, the equivalent resistance across the two corners i.e. B and Cis 1Req=12R+12R.
On solving we get, Req=R. Similarly, equivalent resistance across Aand Dwill also beR.
Hence the equivalent resistance across the opposite corners is R.
Answer: Option D. -> 25
:
D
Given the wire iscut into 5 equal parts.
Let the initial resistance of the wire be R
where R=ρlA→R∝l(lengthofthewire)
then, resistance of each one of the five parts =(R5)
Equivalent resistance (R')of resistorsconnected in parallel is given by1R′=1R1+1R2..1Rn
Equivalent resistance (R') of five parts connected in parallel is given by:
1R′=1(R5)+1(R5)+1(R5)+1(R5)+1(R5)R′=R25
Therefore, RR′=25
:
D
Given the wire iscut into 5 equal parts.
Let the initial resistance of the wire be R
where R=ρlA→R∝l(lengthofthewire)
then, resistance of each one of the five parts =(R5)
Equivalent resistance (R')of resistorsconnected in parallel is given by1R′=1R1+1R2..1Rn
Equivalent resistance (R') of five parts connected in parallel is given by:
1R′=1(R5)+1(R5)+1(R5)+1(R5)+1(R5)R′=R25
Therefore, RR′=25
Answer: Option B. -> 4:1
:
B
Volume of a solid is the product of length and cross-sectional area. V=AL
Since volume is same in both the cases, the length of second wire will be half of the length of 1st wire.
Accordingly, let length of 1st wire = L
area of 1st wire= A = 1mm2
So resistance R=ρLA=ρL1=ρL
Length of the second wire =L2 and
area of 2ndwireA=2mm2
So resistance of 2nd wire R′=ρL2A
R′=ρL2×2
R′=14(ρL)
R′=14(R)
RR′=41
R : R' = 4 : 1
we get the resistance of the 1st wire is 4 times the value of resistance of the 2nd wire.
:
B
Volume of a solid is the product of length and cross-sectional area. V=AL
Since volume is same in both the cases, the length of second wire will be half of the length of 1st wire.
Accordingly, let length of 1st wire = L
area of 1st wire= A = 1mm2
So resistance R=ρLA=ρL1=ρL
Length of the second wire =L2 and
area of 2ndwireA=2mm2
So resistance of 2nd wire R′=ρL2A
R′=ρL2×2
R′=14(ρL)
R′=14(R)
RR′=41
R : R' = 4 : 1
we get the resistance of the 1st wire is 4 times the value of resistance of the 2nd wire.
Answer: Option B. -> electric power
:
B
The physical quantity that determines the rate at which energy is delivered by an electric current is electricpower. The SI unit of electricpower is watt (W). 1 W electrical poweris equivalent to 1 Joule ofelectricalenergy consumed in 1 second time. It is mathematically expressed as P=Et where E is the electrical energyand t is time.
:
B
The physical quantity that determines the rate at which energy is delivered by an electric current is electricpower. The SI unit of electricpower is watt (W). 1 W electrical poweris equivalent to 1 Joule ofelectricalenergy consumed in 1 second time. It is mathematically expressed as P=Et where E is the electrical energyand t is time.