MCQs
Protoplasms And Tissues, Cytoplasmic Membrane Systems, Tissues
Total Questions : 143
| Page 3 of 15 pages
Answer: Option C. -> fluid connective tissue
:
C
There are two types of fluid connective tissues- blood and lymph. Blood circulates throughout the body supplying oxygen, nutrients and removes carbon dioxide and metabolic wastes from the body. Lymph on the other hand, carries materials from the blood stream into tissues and vice-versa. It also kills the pathogens, faciliated by the lymphocytes.
:
C
There are two types of fluid connective tissues- blood and lymph. Blood circulates throughout the body supplying oxygen, nutrients and removes carbon dioxide and metabolic wastes from the body. Lymph on the other hand, carries materials from the blood stream into tissues and vice-versa. It also kills the pathogens, faciliated by the lymphocytes.
Answer: Option A. -> striated muscles
:
A
Muscles that are under the conscious control of an individual are skeletal or striated muscles. For example, the muscles in our arms move only when we want.Such muscles are also called voluntary muscles.
:
A
Muscles that are under the conscious control of an individual are skeletal or striated muscles. For example, the muscles in our arms move only when we want.Such muscles are also called voluntary muscles.
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
Xylem and phloem are two conducting tissues present in plants. Phloem transports food material from leaves to other parts of the plant body. It can conduct food in both directions. Xylem conducts minerals and water only in the upward direction i.e., from roots towards the stem.
:
A
Xylem and phloem are two conducting tissues present in plants. Phloem transports food material from leaves to other parts of the plant body. It can conduct food in both directions. Xylem conducts minerals and water only in the upward direction i.e., from roots towards the stem.
Answer: Option A. -> Opening and closing of stomata
:
A
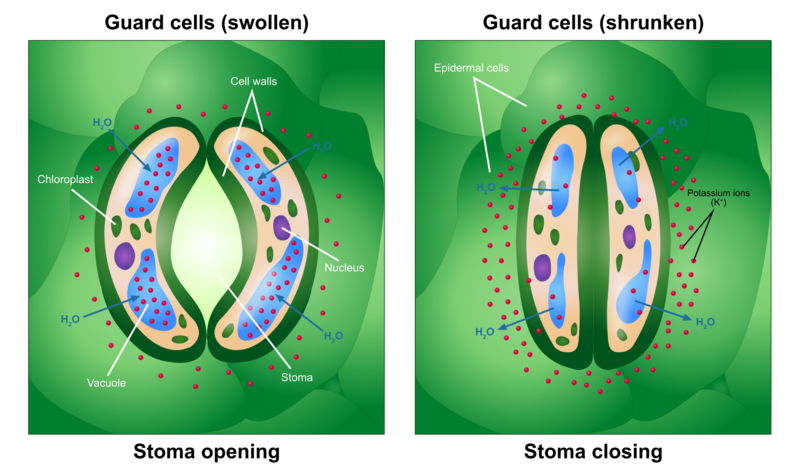
Guard cells are kidney shaped cells that surrounds the stomata. They control the opening and closing of the stomata. When the plant has an excess of water, the guard cells swell and create an opening for the exchange of gases. In dry conditions, the guard cells are flat and keep the stomata closed, inhibiting exchange of gases.
:
A
Guard cells are kidney shaped cells that surrounds the stomata. They control the opening and closing of the stomata. When the plant has an excess of water, the guard cells swell and create an opening for the exchange of gases. In dry conditions, the guard cells are flat and keep the stomata closed, inhibiting exchange of gases.

Answer: Option B. -> adipose tissue
:
B
Adipose tissue is present below the skin and between internal organs. It is a fat storing connective tissue. This layer acts as an insulating layer and shock absorber, protecting the internal organs.
:
B
Adipose tissue is present below the skin and between internal organs. It is a fat storing connective tissue. This layer acts as an insulating layer and shock absorber, protecting the internal organs.
Answer: Option D. -> v-SNARE
Answer: (d).v-SNARE
Answer: (d).v-SNARE
Answer: Option B. -> SNAREs
Answer: (b).SNAREs
Answer: (b).SNAREs
Answer: Option B. -> membrane
Answer: (b).membrane
Answer: (b).membrane
Answer: Option D. -> digestion
Answer: (d).digestion
Answer: (d).digestion
Answer: Option C. -> liver
Answer: (c).liver
Answer: (c).liver
















