General Knowledge > Polity
INDIAN CONSTITUTION AT WORK MCQs
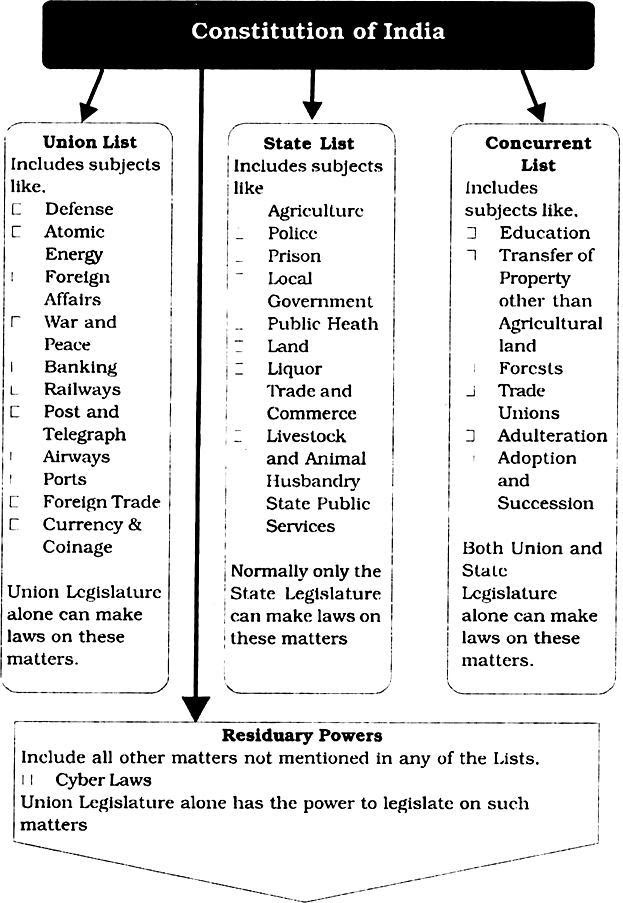
Constitutional Framework, Making Of Indian Constitution And Its Development
Total Questions : 371
| Page 1 of 38 pages
Answer: Option C. -> 1956
:
C
:
C
Answer: Option D. -> All of the above
:
D
:
D
Question 3. Q. Consider the following Statements with reference to Supreme Court:
Which of the above given statements is/are correct?
- All civil authorities within the territory of India act in aid of the Supreme Court.
- The power of Judicial review has not been mentioned in the Constitution but derived from judicial precedents.
Which of the above given statements is/are correct?
Answer: Option A. -> 1 only
:
A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Article 144 states that: all authorities, civil and judicial, in the territory of India shall act in aid of the Supreme Court.
Hence the statement is correct
Statement 2 is Incorrect: Decisions made by theSupreme Court are binding on all other courts within the territory of India. Orders passed by it are enforceable throughout the length and breadth of the country. TheSupreme Court itself is not bound by its decision and can at any time review it. Article 137 states that: the Supreme Court shall have power to review any judgment pronounced or order made by it. Hence the power has been provided in the Constitution. Thus the statement is not correct.
:
A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Article 144 states that: all authorities, civil and judicial, in the territory of India shall act in aid of the Supreme Court.
Hence the statement is correct
Statement 2 is Incorrect: Decisions made by theSupreme Court are binding on all other courts within the territory of India. Orders passed by it are enforceable throughout the length and breadth of the country. TheSupreme Court itself is not bound by its decision and can at any time review it. Article 137 states that: the Supreme Court shall have power to review any judgment pronounced or order made by it. Hence the power has been provided in the Constitution. Thus the statement is not correct.
Answer: Option B. -> Motilal Nehru Committee
:
B
Explanation:
The idea of universal franchise lay securely within the heart of nationalism. As early as the Constitution of India Bill(1895), the first non-official attempt at drafting a constitution for India, the author declared that every citizen, i.e., anyone born in India, had a right to take part in the affairs of the country and be admitted to public office.
Option (a) is incorrect: Fazl Ali Committee was related to Reorganisation of States
Option (b) is correct: The Motilal Nehru Report(1928) reaffirms this conception of citizenship, reiterating that every person of either sex who has attained the age of twenty-one is entitled to vote for the House of Representatives or Parliament.
Option (c) is incorrect: Balwant Rai Mehta Committee was constituted to review community development projects and recommendations related to democratic decentralization and scheme of Panchayati Raj Institutions.
Option (d) is incorrect: The Sarkaria Committee was concerned with Inter state relations.
:
B
Explanation:
The idea of universal franchise lay securely within the heart of nationalism. As early as the Constitution of India Bill(1895), the first non-official attempt at drafting a constitution for India, the author declared that every citizen, i.e., anyone born in India, had a right to take part in the affairs of the country and be admitted to public office.
Option (a) is incorrect: Fazl Ali Committee was related to Reorganisation of States
Option (b) is correct: The Motilal Nehru Report(1928) reaffirms this conception of citizenship, reiterating that every person of either sex who has attained the age of twenty-one is entitled to vote for the House of Representatives or Parliament.
Option (c) is incorrect: Balwant Rai Mehta Committee was constituted to review community development projects and recommendations related to democratic decentralization and scheme of Panchayati Raj Institutions.
Option (d) is incorrect: The Sarkaria Committee was concerned with Inter state relations.
Question 5. Q. With reference to Original jurisdiction of Supreme Court, Consider the following Statements:
Which of the above given statements is/are incorrect?
- It is an exclusive jurisdiction of the Supreme Court.
- Under this, the court can only settle disputes but cannot interpret the powers of Union and State Governments.
- It not only covers disputes between the Union and States but also among the States themselves.
Which of the above given statements is/are incorrect?
Answer: Option D. -> 2 only
:
D
Explanation:
Original jurisdiction means cases that can be directly considered by the Supreme Court without going to the lower courts before that.In any federal country, legal disputes are bound to arise between the Union and the States; and among theStates themselves.
Statement 1 is correct: The power to resolve such cases is entrusted to the Supreme Court of India. It is called original jurisdiction because the Supreme Court alone has the power to deal with such cases.
Statement 2 is Incorrect: In this jurisdiction, the Supreme Court not just settles disputes but also interprets the powers of the Union and State government as laid down in the Constitution.
Statement 3 is correct: In any federal country, legal disputes are bound to arise between the Union and the States; and among the States themselves. The power to resolve such cases is entrusted to the Supreme Court of India.
:
D
Explanation:
Original jurisdiction means cases that can be directly considered by the Supreme Court without going to the lower courts before that.In any federal country, legal disputes are bound to arise between the Union and the States; and among theStates themselves.
Statement 1 is correct: The power to resolve such cases is entrusted to the Supreme Court of India. It is called original jurisdiction because the Supreme Court alone has the power to deal with such cases.
Statement 2 is Incorrect: In this jurisdiction, the Supreme Court not just settles disputes but also interprets the powers of the Union and State government as laid down in the Constitution.
Statement 3 is correct: In any federal country, legal disputes are bound to arise between the Union and the States; and among the States themselves. The power to resolve such cases is entrusted to the Supreme Court of India.
Answer: Option C. -> 1 only
:
C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The 86th Constitutional Amendment (2002) inserted Article 21A in the Indian Constitution which states:
“The State shall provide free and compulsory education to all children of 6 to 14 years in such manner as the State, may by law determine.”
Right to basic and higher education is a part of the South African Constitution as well.
Statement 2 and 3 are Incorrect: Right to Fair Labour Practices and Adequate Housing Which are provided in the South African Bill of Rights, do not form part of Fundamental rights enshrined in Indian Constitution.
:
C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The 86th Constitutional Amendment (2002) inserted Article 21A in the Indian Constitution which states:
“The State shall provide free and compulsory education to all children of 6 to 14 years in such manner as the State, may by law determine.”
Right to basic and higher education is a part of the South African Constitution as well.
Statement 2 and 3 are Incorrect: Right to Fair Labour Practices and Adequate Housing Which are provided in the South African Bill of Rights, do not form part of Fundamental rights enshrined in Indian Constitution.
Question 8. Q. Consider the following:
Which of the above provisions require ratification by states for amendment?
- Amendment of the Constitution to modify Division of powers between Union and States.
- Amendment or Changes in Citizenship.
- Amendments to the process of Election to Parliament and State Legislature.
Which of the above provisions require ratification by states for amendment?
Answer: Option A. -> 1 only
:
A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: For some articles of the Constitution, a special majority is not sufficient. When an amendment aims to modify an article related to distribution of powers between the States and the central government, or articles related to representation, it is necessary that the States must be consulted and that they give their consent.
Statement 2 and 3 are incorrect: A number of provisions in the Constitution can be amended by a simple majority of the two houses of Parliament outside the scope of Article 368. These provisions include:
:
A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: For some articles of the Constitution, a special majority is not sufficient. When an amendment aims to modify an article related to distribution of powers between the States and the central government, or articles related to representation, it is necessary that the States must be consulted and that they give their consent.
Statement 2 and 3 are incorrect: A number of provisions in the Constitution can be amended by a simple majority of the two houses of Parliament outside the scope of Article 368. These provisions include:
- Admission or establishment of new states.
- Formation of new states and alteration of areas, boundaries or names of existing states.
- Abolition or creation of legislative councils in states.
- Second Schedule-emoluments,
- Allowances, privileges and so on of the president, the governors, the Speakers, judges, etc.
- Quorum in Parliament.
- Salaries and allowances of the members of Parliament.
- Rules of procedure in Parliament.
- Privileges of the Parliament, its members and its committees.
- Use of the English language in Parliament.
- Number of puisne judges in the Supreme Court.
- Conferment of more jurisdiction on the Supreme Court.
- Conferment of more jurisdiction on the Supreme Court.
- Citizenship-acquisition and termination.
- Elections to Parliament and state legislatures.
- Delimitation of constituencies.
- Union territories
- Fifth Schedule-administration of scheduled areas and scheduled tribes.
- Sixth Schedule-administration of tribal areas.
Answer: Option A. -> Jammu and Kashmir
:
A
Explanation:
The Constitution has given the States the option of establishing either a unicameral or bicameral legislature. At present only six States have a bicameral legislature:
After the enactment of Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act (2019), the legislative council of Jammu and Kashmir was abolished.
:
A
Explanation:
The Constitution has given the States the option of establishing either a unicameral or bicameral legislature. At present only six States have a bicameral legislature:
- Andhra Pradesh
- Bihar
- Karnataka
- Maharashtra
- Telangana
- Uttar Pradesh
After the enactment of Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act (2019), the legislative council of Jammu and Kashmir was abolished.
Answer: Option D. -> 1 only
:
D
Explanation:
The Government, in January 2015, replaced the Planning Commission with NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) through a Cabinet resolution. It is a non Constitutional and Non Statutory body.
Its aim is to achieve Sustainable Development Goals and to enhance cooperative federalism by fostering the involvement of State Governments of India in the economic policy-making process using a bottom-up approach.
Role of NITI Aayog:The institution has to provide governments at the central and state levels with relevant strategic and technical advice across the spectrum of key elements of policy. This includes matters of national and international import on the economic front, dissemination of best practices from within the country as well as from other nations, the infusion of new policy ideas and specific issue-based support. The institution has to be able to respond to the changing and more integrated world that India is part of.
:
D
Explanation:
The Government, in January 2015, replaced the Planning Commission with NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) through a Cabinet resolution. It is a non Constitutional and Non Statutory body.
Its aim is to achieve Sustainable Development Goals and to enhance cooperative federalism by fostering the involvement of State Governments of India in the economic policy-making process using a bottom-up approach.
Role of NITI Aayog:The institution has to provide governments at the central and state levels with relevant strategic and technical advice across the spectrum of key elements of policy. This includes matters of national and international import on the economic front, dissemination of best practices from within the country as well as from other nations, the infusion of new policy ideas and specific issue-based support. The institution has to be able to respond to the changing and more integrated world that India is part of.