12th Grade > Chemistry
BIOMOLECULES MCQs
Total Questions : 30
| Page 1 of 3 pages
Answer: Option B. -> Configuration
:
B
Option (b)
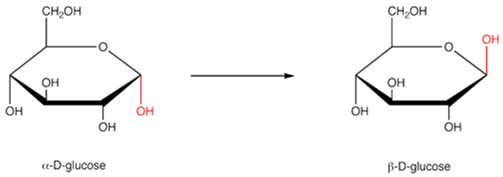
It is clear from the above picture that there is no other difference in these 2 structures other than the difference at the C-1 carbon, which can be attributed to the difference in the configuration of the carbon. This carbon is referred to as the anomeric carbon to highlight this important feature.
:
B
Option (b)

It is clear from the above picture that there is no other difference in these 2 structures other than the difference at the C-1 carbon, which can be attributed to the difference in the configuration of the carbon. This carbon is referred to as the anomeric carbon to highlight this important feature.
Answer: Option C. -> Both
:
C
Option (c)
A substance tht formsZwitter ion can have functional groups −NH2COOH and −NH2−NH2−SO3H
:
C
Option (c)
A substance tht formsZwitter ion can have functional groups −NH2COOH and −NH2−NH2−SO3H
Answer: Option C. -> Saponification
:
C
Option (c)
Oil/fat + Alkali Saponification−−−−−−−−−→ Soap + Glycerol.
:
C
Option (c)
Oil/fat + Alkali Saponification−−−−−−−−−→ Soap + Glycerol.
Answer: Option A. -> Enzymes are specific biological catalysts that cannot be poisoned
:
A
Option (a)
Enzymes are specific biological catalysts that cannot be poisoned.
They are not necessarily heterogeneous catalysts: those in solution in the cellular medium are homogeneous, those bound to a membrane are heterogeneous.
We have seen they perform best at the temeperature close to our normal body temperature around 310 K. At very high temperatures, they become denatured.
:
A
Option (a)
Enzymes are specific biological catalysts that cannot be poisoned.
They are not necessarily heterogeneous catalysts: those in solution in the cellular medium are homogeneous, those bound to a membrane are heterogeneous.
We have seen they perform best at the temeperature close to our normal body temperature around 310 K. At very high temperatures, they become denatured.
Answer: Option D. -> Glycine
:
D
Option (d)
The nine essential amino acids are:histidine isoleucine,leucine, lysine,methionine, phenylalanine,threonine , tryptophan, and valine
:
D
Option (d)
The nine essential amino acids are:histidine isoleucine,leucine, lysine,methionine, phenylalanine,threonine , tryptophan, and valine
Answer: Option C. -> Amino acids
:
C
Option (c)
ProteinEnzyme−−−−−→Aminoacid(Acidicmediuminstomach)
:
C
Option (c)
ProteinEnzyme−−−−−→Aminoacid(Acidicmediuminstomach)
Answer: Option D. -> Glucose and fructose
:
D
Option (d)
C12H22O11Canesugar+H2O→C6H12O6Glucose+C6H12O6Fructose
:
D
Option (d)
C12H22O11Canesugar+H2O→C6H12O6Glucose+C6H12O6Fructose
Answer: Option C. -> Cysteine
:
C
Option (c)
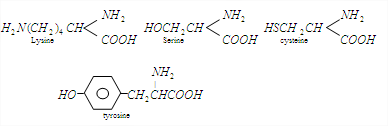
You can clearly see that cysteine is the only amino acid from the options given which contains a sulphur in its structure. You can remember this by going back to the video of the secondary structure of proteins where we talka about the Disulphide linkages which gives shape to the protein sheets.
:
C
Option (c)

You can clearly see that cysteine is the only amino acid from the options given which contains a sulphur in its structure. You can remember this by going back to the video of the secondary structure of proteins where we talka about the Disulphide linkages which gives shape to the protein sheets.
Answer: Option A. -> Cellulose
:
A
We cannot digest cellulose, which is a polysaccharide. Our digestive system is not capable of digesting this tough carbohydrate. However, herbivorous animals like cows are well-equipped to do just that.
:
A
We cannot digest cellulose, which is a polysaccharide. Our digestive system is not capable of digesting this tough carbohydrate. However, herbivorous animals like cows are well-equipped to do just that.